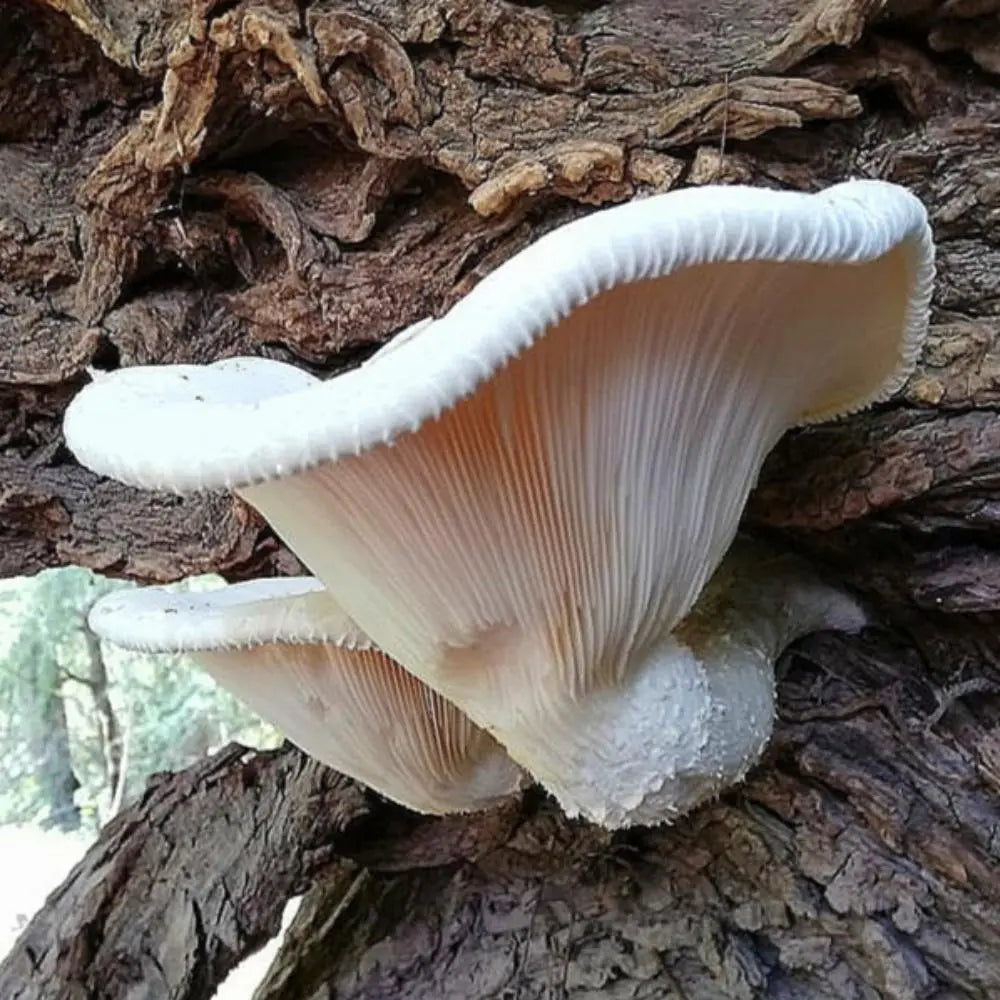
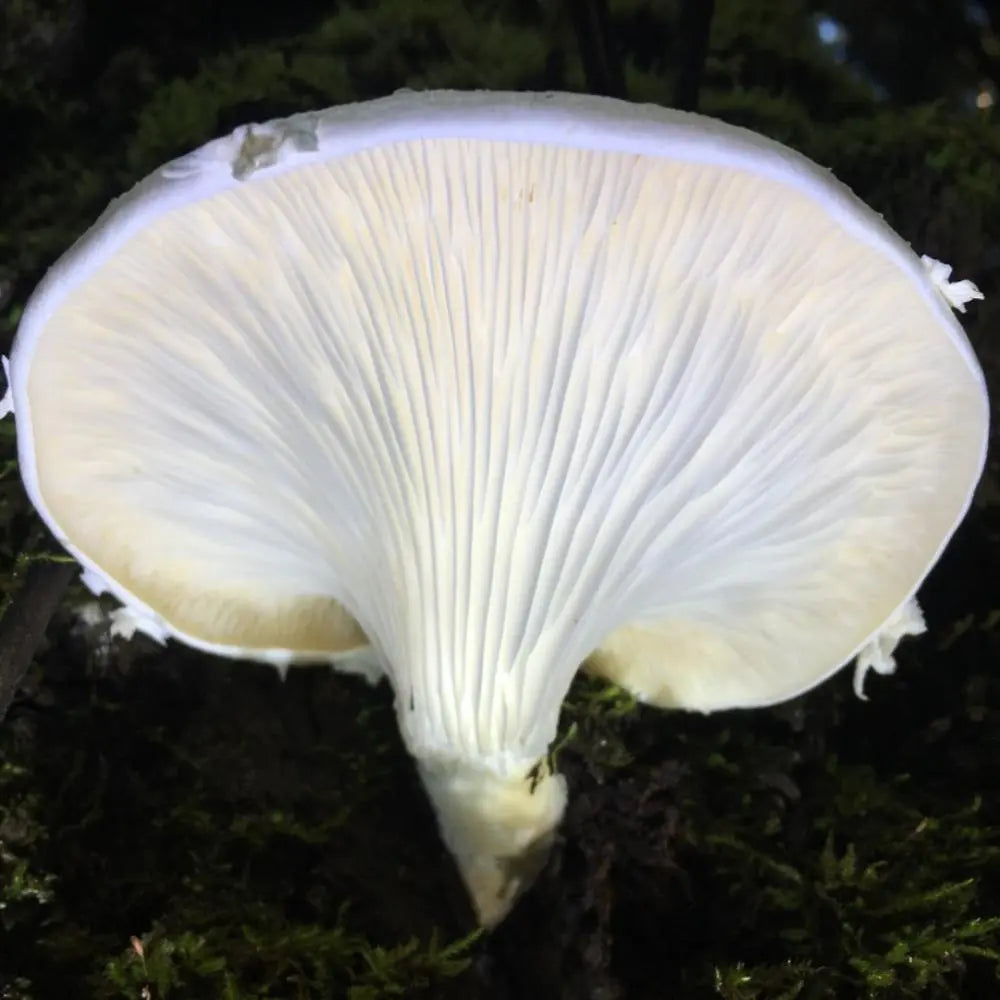
Antibacterial Effects
Research into the antibacterial properties of mushrooms is a growing field, driven by the need for alternative strategies to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Many mushroom species produce bioactive compounds, such as terpenoids, phenolics, polysaccharides, and alkaloids, which exhibit significant antibacterial activity. These compounds can disrupt bacterial cell walls, inhibit protein synthesis, and interfere with quorum sensing, a process critical for bacterial communication and virulence.
Research is also focused on identifying new compounds through advanced techniques like metabolomics and bioinformatics, which can reveal previously unknown antibacterial molecules. Combining mushroom extracts with existing antibiotics to enhance efficacy and reduce resistance is another promising direction.